

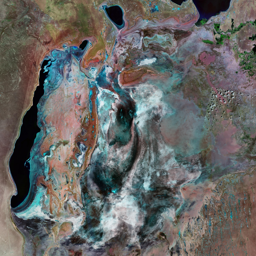
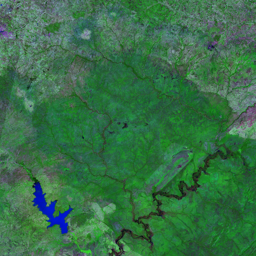






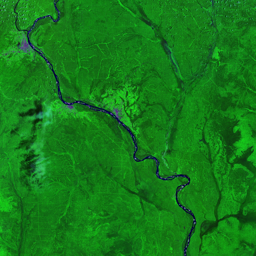



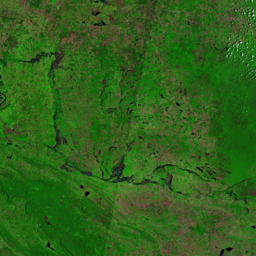
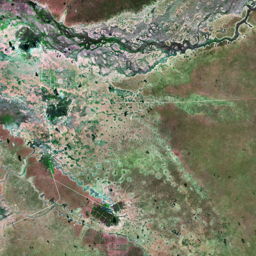

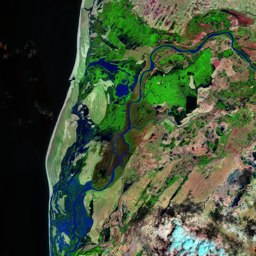



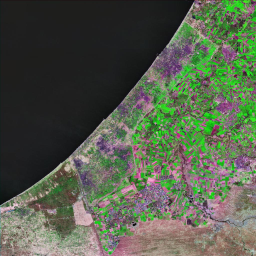


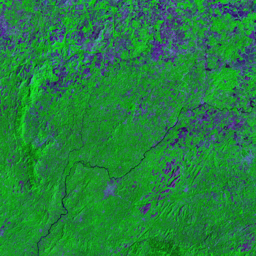


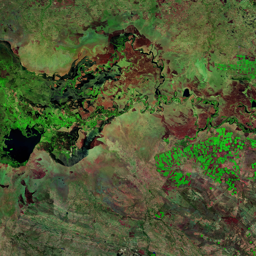
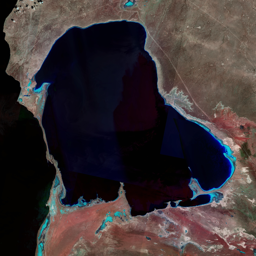
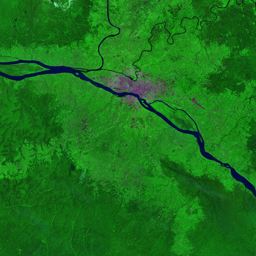


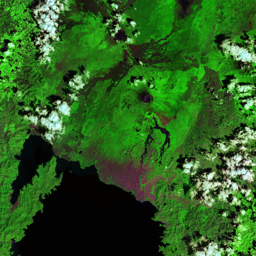


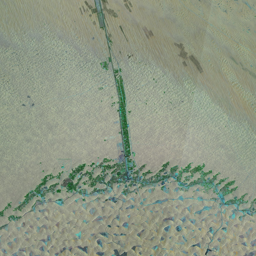

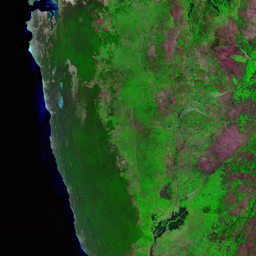


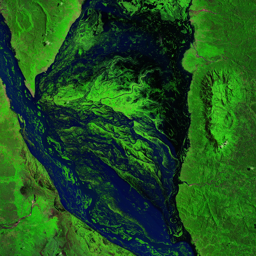





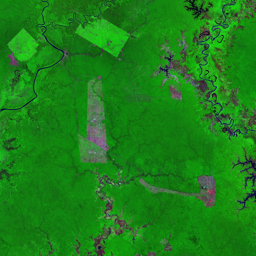

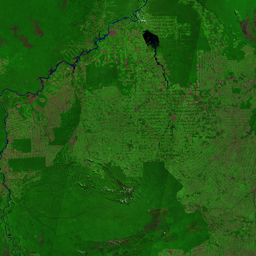





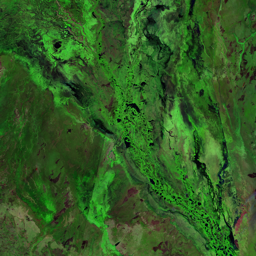



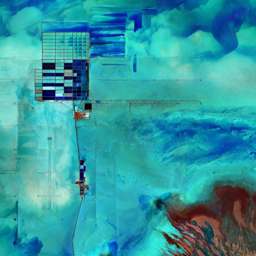

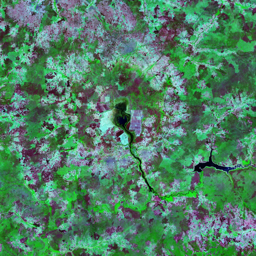
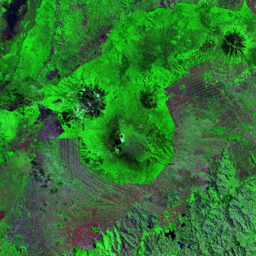




The Catoca kimberlite pipe (diamond-rich geological formations) in the Lunda Sul province of Angola is the world's fourth largest in terms of surface area, with diamond reserves of at least 40 million carats. The Catoca Mine was constructed between 1994 and 1997. In 2003, the mine produced 2.5 million carats worth US$ 189 million. Mining, by its very nature, significantly alters the landscape. Satellite images show the extent of change at Catoca over several decades of exploitation. Diamond mining is a large-scale earth-moving operation-for each carat recovered, more than a tonne of material is moved. Diamond mining is also extremely water intensive, since water is used to wash the final gravels and separate the diamonds. The Catoca Mine was built to minimize its environmental footprint. The first extraction methods produce little toxic waste. The next stage of the project, however, uses dense media separation (DMS) for diamond recovery, a chemical process that exerts a far greater environmental impact. In the mine surrounding you can also notice how slash-and-burn practice quickly change the landscape
Use shift + scroll to zoom the map
Use shift + scroll to zoom the map